So, you’re just looking at your website in google search console, checking if everything looks good. The next thing you know is you’ve got a bunch of 404 errors. And now you’re left wondering what to do next.
Most people slip into fear when they encounter unexplained 404 errors on their website. But is it a bad thing? Can a 404 error impact your ranking, or is it just a normal part of website maintenance? Let’s find out.
Table of contents
- What is a 404 Error?
- What Are Hard and Soft 404 Errors?
- What Happens to a 404 Page on a Search Engine?
- Do 404 Errors Affect Google Rankings?
- When You Should (and Shouldn’t) Fix 404 Errors?
- How 404 Errors Impact User Experience
- Lost Link Equity Due to 404 Errors
- Hard 404 vs. Soft 404: Why It Matters
- Best Practices for Handling 404 Errors
What is a 404 Error?
A 404 error occurs when a user or search engine requests a URL that your server cannot provide. The client may have deleted the page, entered the address incorrectly, or clicked on a broken link. In such situations, the server sends back a status code 404 which indicates Page Not Found.
What Are Hard and Soft 404 Errors?
There are two types of 404 errors:
- Hard 404: The server returns a 404 status code, indicating that the page does not exist.
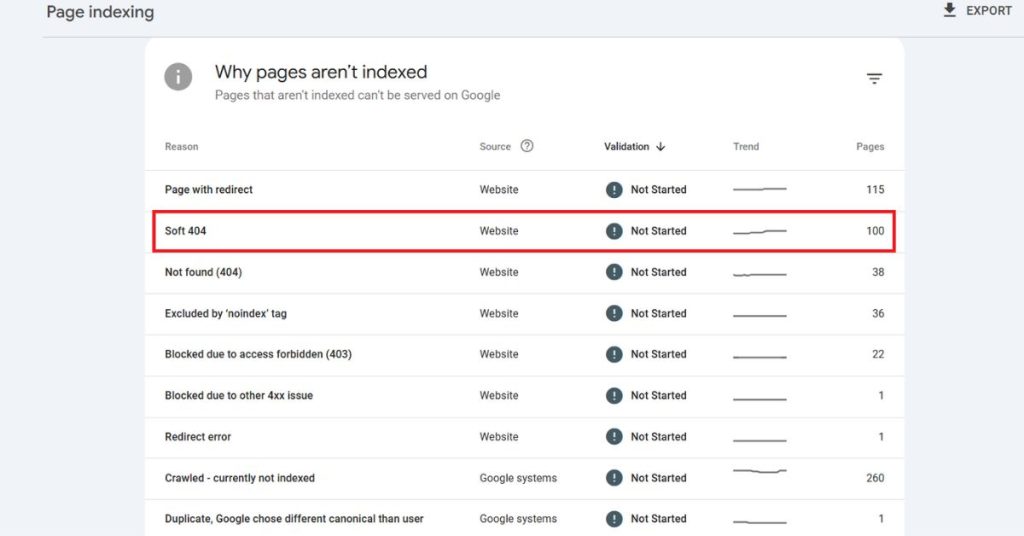
- Soft 404: A page that is said to exist returns a 200 OK status. However, a vague error message or no content is displayed. This is also an error in its own right because search engines expect a value for a technically “found” page, but instead get no value.
What Happens to a 404 Page on a Search Engine?
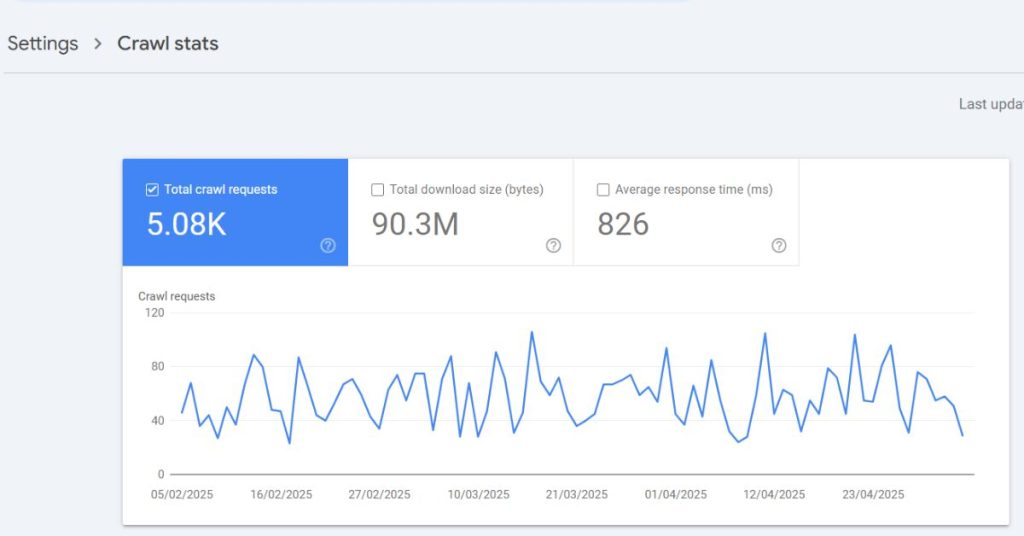
Search engines, like Google, comprehend how sites change over time, with some pages being deleted. They recognize that once in a while, a 404 error may show up, and these do not cause significant damage to your SEO. Googlebot, for example, understands that if it runs into a 404 (not found) or 410 (content lost) error, it can expect that URL to be omitted from its listing in due course.
That said, the presence of excessive or repetitive 404 errors can prove detrimental to your crawl budget; the total number of pages Googlebot gets indexed on your site within a particular period. The more time crawlers take on dead 404 pages, the less time they have to access, index, and discover information that is actually useful.
Do 404 Errors Affect Google Rankings?
Well, this depends on the context.
Google assigns a crawl budget for each website, which is the number of pages it will crawl within a certain period. If Googlebot encounters multiple 404 pages, it wastes crawl resources on non-existent content instead of discovering your new or updated pages.
Now, this inefficiency can delay the indexing of important content, indirectly affecting SEO performance. Ensuring your site has minimal 404 errors helps Google crawl your site more effectively.
When You Should (and Shouldn’t) Fix 404 Errors?
Times when 404s need to be looked at:
- Having other pages link to 404 pages creates poor internal structures, which hurt the user and crawler experience.
- Losing access to pages that have significant backing links results in losing valuable beneficial link equity, ultimately diminishing the site’s authority.
- Having multiple 404s on your website makes it harder for users and crawlers to navigate the website, indirectly impacting website ranking.
When 404s are fine:
- Deleting pages that are irrelevant means users expect 404s, making them acceptable.
- Not having any external links pointing to deleted pages does not impact the rating of your site.
- There is always content that signals to search engines that redirecting to non-existent URLs is better than repurposing existing content.
How 404 Errors Impact User Experience
Encountering a 404 error page as a user is quite irritating. Stopping at dead ends while trying to navigate and access content results in broken pathways for user movement that frustrate users, which increases bounce rates. Google checks how users interact and engage with your site. Interacting poorly with your website will inevitably lower your ranking.
Such as loss of trust can also come from domains displaying non-informative text, “404, page not found,” which creates voids without context and enhances loss of user trust. Users are simply offered a dead 404 page, which doesn’t do anything, severely damaging trust.
Solution: Add active links for navigation on your 404 error pages so users can interact with them and remain interested.
Lost Link Equity Due to 404 Errors
Authority passed from one page to another through backlinks is called “link equity” or “link juice”. If the page with the backlinks has a 404 page, this equity diminishes because the page is no longer there to transfer value.
The strength of your website’s authority may be negatively affected due to this loss, which will contribute to lowering your ranking.
Hard 404 vs. Soft 404: Why It Matters
For maintaining a site’s SEO health, it is important to grasp the concept of hard and soft 404s.
- Hard 404: The server 404 hard codes a page not found or returns an error message indicating the requested page is not available. This is the correct way to handle non-existent pages.
- Soft 404: A soft 404 tells you that the page is available but serves little to no content. Google recognizes that these pages do exist, but brandishes them as errors because they do not serve any real purpose.
Now, soft 404’s do pose some threats because they make it difficult for Googlebot to traverse pages posing as an overly complicated maze. Moreover, they are capable of bloating an index and degrading site-wide signals of site integrity.
How to Fix Soft 404s
- Make sure status codes are accurate: Pages that have been deleted or are missing should have a status of 404 or 410 Gone.
- Using 301 redirects: If content has been changed or replaced, the old URL can be redirected to the new relevant page to maintain online authority and link equity.
- Scrapping low-quality pages: Pages that have little to no content must be deleted or improved by adding valuable information.
Best Practices for Handling 404 Errors
The key to minimizing SEO damage from 404 errors is proactive monitoring, fixing broken links, implementing proper redirects, and creating user-friendly custom 404 pages. By managing 404 errors effectively, you maintain a healthy site structure, improve user experience, and protect your search engine rankings.
Regularly Monitor 404 Errors: Use tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs to identify broken links and 404 pages.
Fix Broken Internal Links: Update or remove internal links pointing to 404 pages to maintain a clean site structure.
Implement 301 Redirects: Redirect important deleted pages to relevant alternatives to retain SEO value and guide users.

Create a Custom 404 Page: Design a helpful, branded 404 page with navigation options, search functionality, and links to popular content.
Keep Your Sitemap Updated: Remove URLs of deleted pages from your XML sitemap to avoid confusing search engines.
Audit Backlinks: For pages with valuable backlinks that return 404, consider restoring content or redirecting to maintain link equity.
When to Let 404s Be
Not all 404 errors need fixing. If a page is outdated, irrelevant, or has no traffic or backlinks, it’s often best to leave it as a 404. This tells the Google to drop the page from indexing and prevents unnecessary redirects.
Final Verdict
It’s true that 404 errors are a natural part of website management and are not inherently bad for SEO. Occasional 404s, especially for removed or outdated content, are expected and do not harm your site’s rankings. However, unmanaged or excessive 404 errors-especially those caused by broken internal links or pages with backlinks-can negatively impact your SEO by wasting crawl budget, losing link equity, and frustrating users.
Ready to improve your website’s SEO health? Get expert help with SEO agency NZ, auditing your 404 errors today and turning those dead ends into opportunities for growth.